▒█████ █████▒ █████▒ ██████ ▓█████ ▄████▄ ██▒ █▓ ▄▄▄ █ ██ ██▓ ▄▄▄█████▓
▒██▒ ██▒▓██ ▒▓██ ▒▒██ ▒ ▓█ ▀ ▒██▀ ▀█▓██░ █▒▒████▄ ██ ▓██▒▓██▒ ▓ ██▒ ▓▒
▒██░ ██▒▒████ ░▒████ ░░ ▓██▄ ▒███ ▒▓█ ▄▓██ █▒░▒██ ▀█▄ ▓██ ▒██░▒██░ ▒ ▓██░ ▒░
▒██ ██░░▓█▒ ░░▓█▒ ░ ▒ ██▒▒▓█ ▄ ▒▓▓▄ ▄██▒▒██ █░░░██▄▄▄▄██ ▓▓█ ░██░▒██░ ░ ▓██▓ ░
░ ████▓▒░░▒█░ ░▒█░ ▒██████▒▒░▒████▒▒ ▓███▀ ░ ▒▀█░ ▓█ ▓██▒▒▒█████▓ ░██████▒▒██▒ ░
░ ▒░▒░▒░ ▒ ░ ▒ ░ ▒ ▒▓▒ ▒ ░░░ ▒░ ░░ ░▒ ▒ ░ ░ ▐░ ▒▒ ▓▒█░░▒▓▒ ▒ ▒ ░ ▒░▓ ░▒ ░░
░ ▒ ▒░ ░ ░ ░ ░▒ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ▒ ░ ░░ ▒ ▒▒ ░░░▒░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ▒ ░ ░
░ ░ ░ ▒ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░░ ░ ▒ ░░░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░
░ ░ ░ ░ ░░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░ ░
░ ░
ELF Architecture
library extension in Linux: .so | equivalent to .dll for Windows
composition:
-* ELF header
a ELF file, can be identified by the "Magic Bytes", 4 bits that are always the same for a ELF file.
ASCII = .ELF
HEX = 7f 45 4c 46
 color purple means: ELF version, only exist version 1
>>> identify if the file is 32bit or 64bit [blue] 0x02 for 64bit
>>> identify if the file is big-endian or little-endian [red] 0x01 for little-endian
>>> identify if the file is executable, library, etc
>>> identify entry point of the application [ _start ]
types:
EXEC for executables [no position-independent code]
DYN for library or executables supporting position-independent code
REL for Object File
CORE for Core dumps
color purple means: ELF version, only exist version 1
>>> identify if the file is 32bit or 64bit [blue] 0x02 for 64bit
>>> identify if the file is big-endian or little-endian [red] 0x01 for little-endian
>>> identify if the file is executable, library, etc
>>> identify entry point of the application [ _start ]
types:
EXEC for executables [no position-independent code]
DYN for library or executables supporting position-independent code
REL for Object File
CORE for Core dumps
-* Program Header Table
segments = execution
::::headers
:type = p_type [man page] | LOAD & GNU_STACK
:offset = specifies where in the ELF file the content of the segment is located
:VirtAddr = specifies where the first byte of the segment will be in memory
:FileSiz = specifies the size of the segment in the ELF file
:MemSiz = specifies the size of the segment in memory. [if is larger than FileSiz, then the letfover byter
will be initialized to 0]
:Flags = [R/W/E] permissions
-* Segments & Sections
ELF file needs two types of information:
data for linking = sections
data for execution = segments
sections = linking | segments = execution
segments & sections are relevant as both are data in a file, however the relevance differs:
segments describe how the data has to be loaded into memory.
importants segments:
data segment: contains initialized & uninitialized data and global variables
code segment: contains executable code
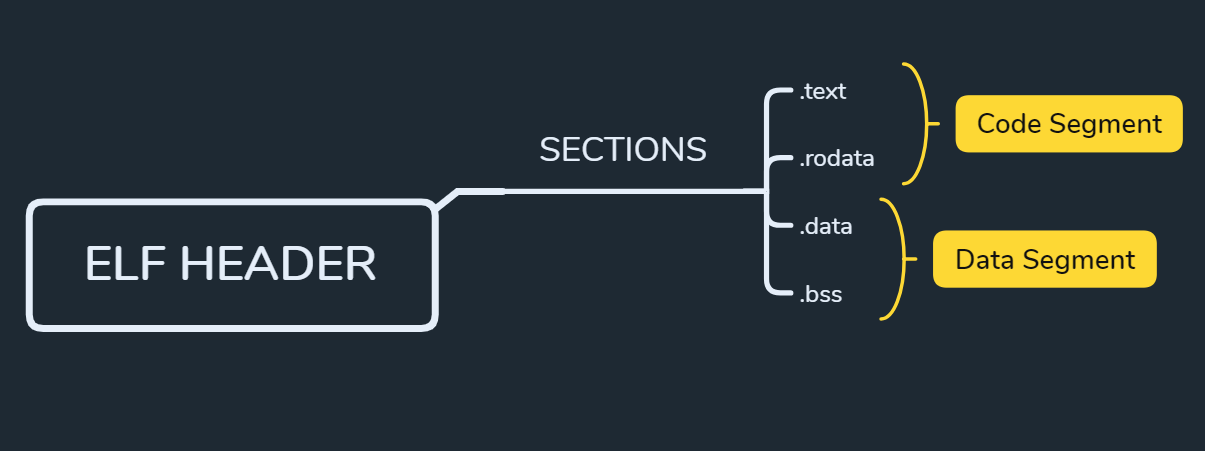
-* Section Header Table
contains information like,
::: headers
:Name = name of the file header
:type = sh_type [man page]
:Address = specifie where the section will appear within the memory image of a process [flags | link |
info]
:Offset = starting point
:Size = section size
sections = linking
important sections:
--: SHT_PROGBITS
.data = initialized global & static variables [r/w] permissions
.rodata = same as .data however it is read-only
.bss = uninitialized variables
.got = global offset table, enable position independent code
.plt.got = address of functions--: SHT_HASH
--: SHT_STRTAB
.strtab
.shstrtab
 color purple means: ELF version, only exist version 1
>>> identify if the file is 32bit or 64bit [blue] 0x02 for 64bit
>>> identify if the file is big-endian or little-endian [red] 0x01 for little-endian
>>> identify if the file is executable, library, etc
>>> identify entry point of the application [ _start ]
types:
EXEC for executables [no position-independent code]
DYN for library or executables supporting position-independent code
REL for Object File
CORE for Core dumps
color purple means: ELF version, only exist version 1
>>> identify if the file is 32bit or 64bit [blue] 0x02 for 64bit
>>> identify if the file is big-endian or little-endian [red] 0x01 for little-endian
>>> identify if the file is executable, library, etc
>>> identify entry point of the application [ _start ]
types:
EXEC for executables [no position-independent code]
DYN for library or executables supporting position-independent code
REL for Object File
CORE for Core dumps
